Paid-in capital is the actual investment by the stockholders; retained earnings is the investment by the stockholders through earnings not yet withdrawn. When a company pays dividends to its shareholders, it reduces its retained earnings by the amount of dividends paid. It reconciles the beginning balance of net income or loss for the period, subtracts dividends paid to shareholders and provides the ending balance of retained earnings. Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings or profits of a company after accounting for dividend payments.
How a Stock Dividend Works

Movements in a company’s equity balances are shown in a company’s statement of changes in equity, which is a supplementary statement that publicly traded companies are required to show. Both the beginning and ending retained earnings would be visible on the company’s balance sheet. The ultimate effect of cash dividends on the company’s balance sheet is a reduction in cash for $250,000 on the asset side, and a reduction in retained earnings for $250,000 on the equity side. After the dividends are paid, the dividend payable is reversed and is no longer present on the liability side of the balance sheet. When the dividends are paid, the effect on the balance sheet is a decrease in the company’s retained earnings and its cash balance.
Cash Dividend Example
If a company has a net loss for the accounting period, a company’s retained earnings statement shows a negative balance or deficit. A statement of retained earnings is a formal statement showing the items causing changes in unappropriated and appropriated retained earnings during a stated period of time. Changes in unappropriated retained earnings usually consist of the addition of net income (or deduction of net loss) and the deduction of dividends and appropriations. Changes in appropriated retained earnings consist of increases or decreases in appropriations. Cash dividends are a distribution of a corporation’s earnings to its stockholders or shareholders.

Impact of Dividends on Retained Earnings
A stock dividend is considered small if the shares issued are less than 25% of the total value of shares outstanding before the dividend. A journal entry for a small stock dividend transfers the market value of the issued do dividends decrease retained earnings shares from retained earnings to paid-in capital. Retained earnings represent the total profit to date minus any dividends paid.Revenue is the income that goes into your business from selling goods or services.

Retained earnings represent a key measure of a company’s accumulated net income, after accounting for dividends paid to shareholders. This financial metric offers insight into the firm’s historical profitability and its capacity to fund internal projects or pay down debt. Because cash dividends are not a company’s expense, they show up as a reduction in the company’s statement of changes in shareholders’ equity.
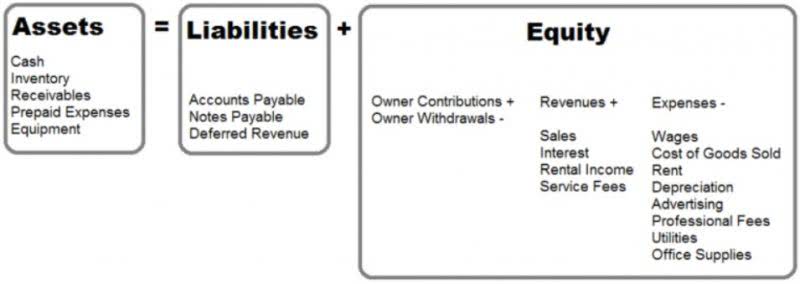
- Net income refers to the company’s total profit after all expenses, while retained earnings are the portion of that profit that the company keeps rather than distributing as dividends.
- Dividends, whether cash or stock, represent a reward to investors for their investment in the company.
- Your accounting software will handle this calculation for you when it generates your company’s balance sheet, statement of retained earnings and other financial statements.
- If an investor is looking at December’s financial reporting, they’re only seeing December’s net income.
- A stock’s par value is a nominal face value — often a penny or less per share — that’s required by law in many states.
- Say your company has 10,000 shares outstanding with a par value of 5 cents and will distribute 1,000 new shares at the market price of $15 a share.
Also, this outflow of cash would lead to a reduction in the retained earnings of the company as dividends are paid out of retained earnings. Some companies, particularly those in high-growth industries, may reinvest https://www.bookstime.com/ all of their profits back into the business to fund expansion, research and development, or debt repayment. In such cases, the company’s earnings are retained rather than distributed to shareholders.
- If it instead issues a 10% stock dividend, the same investor receives 10 additional shares, and the company doles out 100,000 new shares in total.
- This is the case where the company has incurred more net losses than profits to date or has paid out more dividends than what it had in the retained earnings account.
- They’re like a link between your income statement (aka your profile and loss statement) and your balance sheet.
- The money that’s left after you’ve paid your shareholders is held onto (or “retained”) by the business.
- Retained earnings provide a much clearer picture of your business’ financial health than net income can.
Find your net income (or loss) for the current period

